L
lisica198808
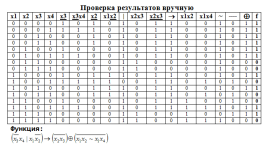
Скажу честно - программу переделывала под свою, ту которую нашла в интернете.Добавила пару нужных мне функций, и поисправляла ошибки.Запускается - работает. но несколько данных не сходятся с моим ручным просчетом. то что я в ручную правильно все сделала - я уверена.а почему не все данные сходятся - не понимаю прилагаю скрин своей ручной работы, формулу по которой делала прогу, и сам код программы.
тема реализации программы : Логические функции переменных (дискретка)
Скрин с формулой - в файлике. немного не разобралась как картинки скидывать
тема реализации программы : Логические функции переменных (дискретка)
C++:
#include <iostream.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int * CycleNot(int,int,int,int); //0// отрицание
int * CycleAnd(int,int,int,int); //1// умножение (коньъюнкция)
int * CycleXor(int,int,int,int); //2// сложение |2|
int * CycleNor(int,int,int,int); //4// стрелка Пирса
int * CycleNors(int,int,int,int); //5// Шефнер
int * CycleImpl(int,int,int,int); //6// импликация
int * CycleEkv(int,int,int,int);//7// эквиваленция
int Not(int x) // отрицание
{
if (x)
return 0;
return 1;
}
int And(int x, int y) // умножение (коньъюнкция)
{
return x*y;
}
int Xor(int x, int y) // сложение |2|
{
if (x!=y)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int Nor(int x, int y) // стрелка Пирса
{
if (x==0 && y==0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int Nors(int x, int y) // Шефнер
{
if (x==1 && y==1)
return 0;
return 1;
}
int Impl(int x, int y) // импликация
{
if (x==1 && y==0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
int Ekv(int x, int y) // эквиваленция
{
if (x=y)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// функции циклов обработки по формулам
int * CycleNot(int *x)
{
int *z = new int[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
*(z+i) = Not(x[i]);
}
return z;
}
int * CycleAnd(int *x,int *y)
{
int *z = new int[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
*(z+i) = And(x[i],y[i]);
}
return z;
}
int * CycleXor(int *x,int *y)
{
int *z = new int[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
*(z+i) = Xor(x[i],y[i]);
}
return z;
}
int * CycleNor(int *x,int *y)
{
int *z = new int[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
*(z+i) = Nor(x[i],y[i]);
}
return z;
}
int * CycleNors(int *x,int *y)
{
int *z = new int[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
*(z+i) = Nors(x[i],y[i]);
}
return z;
}
int * CycleImpl(int *x,int *y)
{
int *z = new int[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
*(z+i) = Impl(x[i],y[i]);
}
return z;
}
int * CycleEkv(int *x,int *y)
{
int *z = new int[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
*(z+i) = Ekv(x[i],y[i]);
}
return z;
}
// -=Программа=-
int main()
{
// инициализация переменных
int x1[16] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1};
int x2[16] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1};
int x3[16] = {0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1};
int x4[16] = {0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1};
int *temp1;
int *temp2;
int *temp3;
int *temp4;
temp1 = CycleNot(x3);
temp2 = CycleAnd(temp1,x4);
temp1 = CycleNot(x2);
temp3 = CycleAnd(x1,temp1);
temp1 = CycleNors(temp2,temp3);
temp2 = CycleAnd(x2,x3);
temp3 = CycleNot(temp2);
temp2=CycleImpl(temp1,temp3);
temp1=CycleAnd(x1,x2);
temp3=CycleAnd(x1,x4);
temp4=CycleEkv(temp1,temp3);
/*ekv*/
temp1 = CycleXor(temp2,temp4);
cout << "-------------\nx1 x2 x3 x4 f\n-------------";
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) // выводим функцию на экран
{
cout << endl << x1[i] << " ";
cout << x2[i] << " ";
cout << x3[i] << " ";
cout << x4[i] << " ";
cout << temp1[i] << endl;
}
cout << "-------------";
cout << "\n\n SDNF: ";
int f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) //'"Ќ"
{
if (temp1[i]==1)
{
f++;
if (!x1[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x1*";
if (!x2[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x2*";
if (!x3[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x3*";
if (!x4[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x4";
if (i<15) cout << " + ";
if (f==4 || f==8 || f==12) cout << endl << " ";
}
}
cout << "\n\n SKNF: ";
f = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) //'ЉЌ"
{
if (temp1[i]==0)
{
f++;
cout << "(";
if (x1[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x1+";
if (x2[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x2+";
if (x3[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x3+";
if (x4[i]) cout << "!";
cout << "x4";
cout << ") ";
if (f==4 || f==8 || f==12) cout << endl << " ";
}
}
cout << "\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}Скрин с формулой - в файлике. немного не разобралась как картинки скидывать